Rainwater Harvesting System for Household or Homestead Water Supply
Reducing dependency on municipal water and embracing sustainable practices are key goals for many homeowners today. One effective way to achieve this is by setting up a comprehensive rainwater collection system for household use. Such systems not only save money but also provide a reliable alternative water source for various household needs.
Rainwater, free from many chemicals found in tap water, offers a cleaner option for drinking, cooking, and bathing. Implementing a rainwater harvesting system in your home can lead to significant long-term benefits, contributing to both environmental conservation and self-sufficiency. Let’s delve into how you can set up and maintain a rainwater collection system that meets your household’s needs.
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting
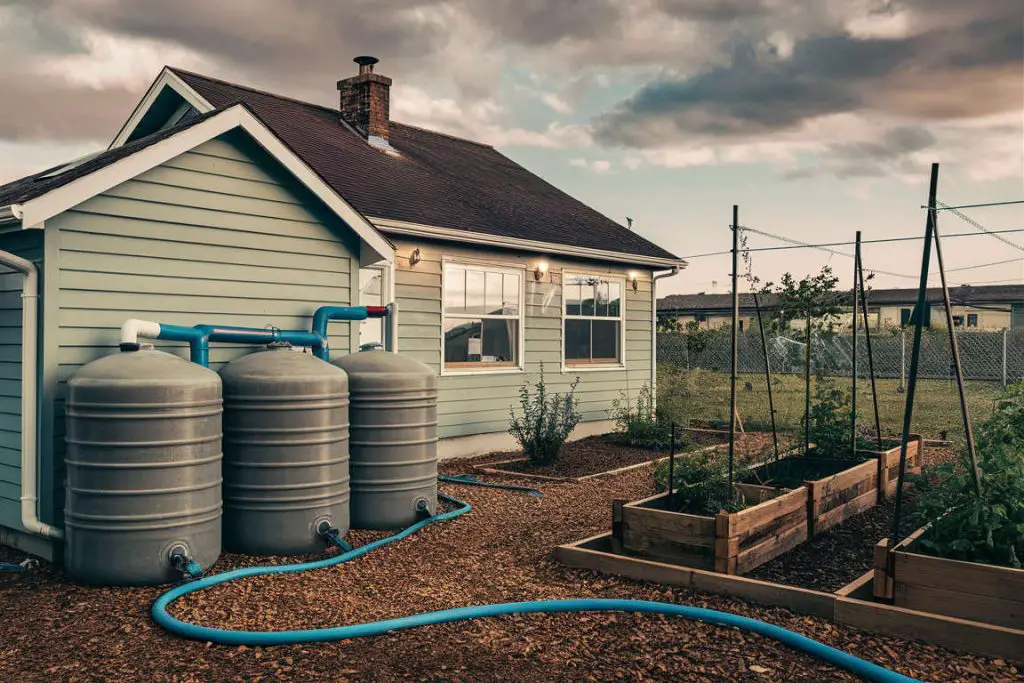

Rainwater harvesting involves capturing, storing, and using rainwater for household needs. It’s a sustainable practice that offers numerous advantages, including reduced reliance on municipal water supplies and lower water bills. The process starts with collecting rainwater from your roof through gutters and downspouts, directing it into storage tanks. From there, the water can be filtered and treated to make it safe for household use.
Legal considerations and regulations play a crucial role in implementing a rainwater harvesting system. Local laws may dictate the types of systems allowed and the necessary permits. It’s essential to research and understand these regulations to ensure compliance. Adhering to these guidelines helps in setting up a system that is both effective and legally sound.
System Design and Planning
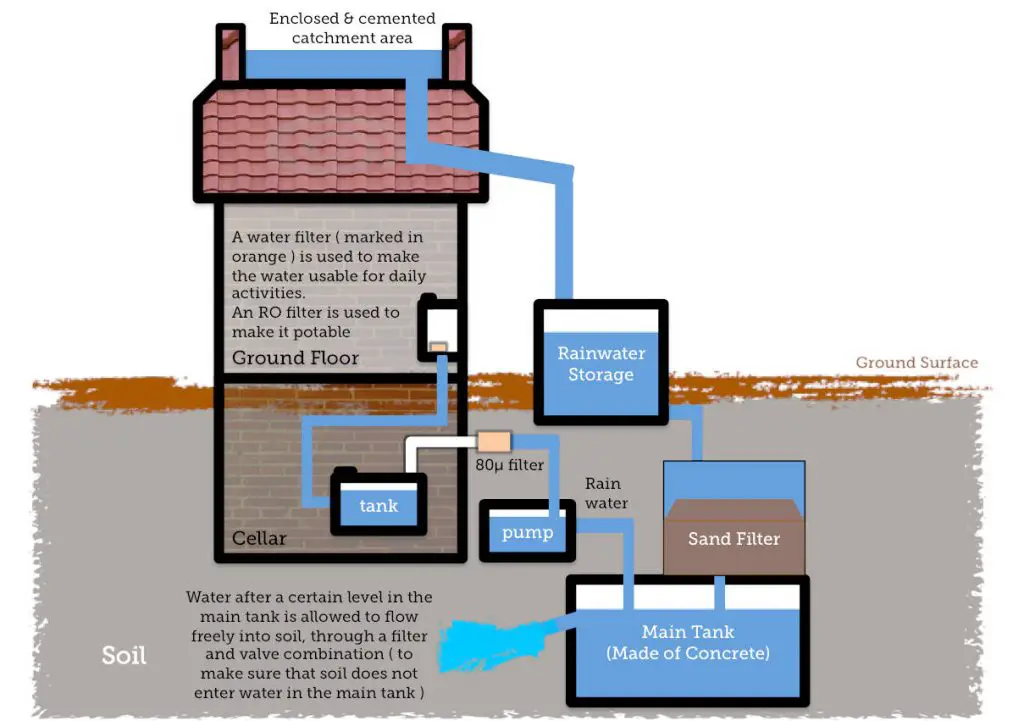
Designing a rainwater collection system requires careful planning. When you are looking to supply both garden and household needs the system will likely be more extensive than a rainwater system that only needs to supply the garden
Start by calculating your household’s water needs and the typical rainfall in your area. This information will help determine the size of the storage tanks and the necessary components. Larger households or areas with low rainfall may need more extensive systems to meet their water needs.
Calculating Water Needs and Rainfall
Understanding your household’s water requirements and local rainfall patterns is essential for designing an efficient system:
- Water Usage Assessment: Estimate your household’s daily, monthly, and annual water consumption. Consider all uses, including drinking, cooking, bathing, and irrigation.
- Rainfall Analysis: Analyze local rainfall data to determine the average annual rainfall and seasonal variations. This information helps in estimating the volume of water you can collect.
- Storage Capacity: Based on your water usage and rainfall analysis, calculate the required storage capacity. Ensure the storage tanks can hold enough water to meet your needs during dry periods.
Choosing the Right Components
Selecting appropriate components is crucial for the system’s efficiency and longevity:
- Storage Tanks: Choose tanks made from durable, food-grade materials to ensure water quality. Consider tank size, shape, and placement options.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Install high-quality gutters and downspouts that can handle the expected volume of water. Ensure they are properly sized and securely attached to the roof.
- Filters and Diverters: Include first flush diverters, sediment filters, and other filtration systems to maintain water cleanliness. These components help remove debris and contaminants from the collected rainwater.
- Pumps and Piping: Select pumps that provide adequate water pressure for household use. Use durable, UV-resistant pipes to connect the system components.
Positioning and Installing Components
Strategically positioning and installing system components ensures efficient water collection and distribution:
- Tank Placement: Position storage tanks close to the house for easy access and efficient water flow. Elevated platforms can enhance gravity-fed systems.
- Gutter Installation: Attach gutters along the roof edge, ensuring they slope towards the downspouts for optimal water collection.
- Downspout Connection: Connect downspouts to the gutters and direct them towards the storage tanks. Securely attach all components to prevent leaks and ensure stability.
- Overflow Management: Install overflow outlets on storage tanks to handle excess water during heavy rains. Direct overflow to safe drainage areas or secondary storage tanks.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Adhering to local regulations and guidelines is essential for a legally compliant system:
- Permits and Approvals: Check local laws and obtain necessary permits before installing the system. Regulations may vary depending on location and system size.
- Building Codes: Ensure the system design complies with building codes and safety standards. This includes proper installation of electrical components and structural supports.
- Health and Safety Standards: Follow health and safety guidelines to prevent contamination and ensure water quality. Regularly inspect and maintain the system to meet these standards.
Integrating with Existing Infrastructure
Seamlessly integrating the rainwater collection system with existing household infrastructure enhances functionality:
- Plumbing Integration: Connect the rainwater system to the household plumbing using valves and control systems. This setup allows switching between rainwater and municipal water as needed.
- Backup Systems: Implement backup systems to ensure a continuous water supply during low rainfall periods. This can include secondary tanks or connections to well water.
- Monitoring and Control: Install sensors and control systems to monitor water levels and quality. Automated systems can manage water flow and alert you to maintenance needs.
Planning for Maintenance and Scalability
Designing a system that is easy to maintain and scalable ensures long-term reliability and adaptability:
- Maintenance Access: Design the system with easy access to all components for regular maintenance. This includes accessible filters, diverters, and tank cleaning points.
- Scalability: Plan for future expansion by choosing components that can accommodate increased water storage and usage. This allows you to scale up the system as your household needs grow.
- User Training: Educate household members on system operation and maintenance. Understanding how to manage the system ensures its longevity and effectiveness.
System design and planning are critical steps in creating an efficient and reliable rainwater collection system for household use. Following these guidelines helps ensure the system meets your needs, complies with regulations, and remains sustainable over the long term.
Installing the Collection System
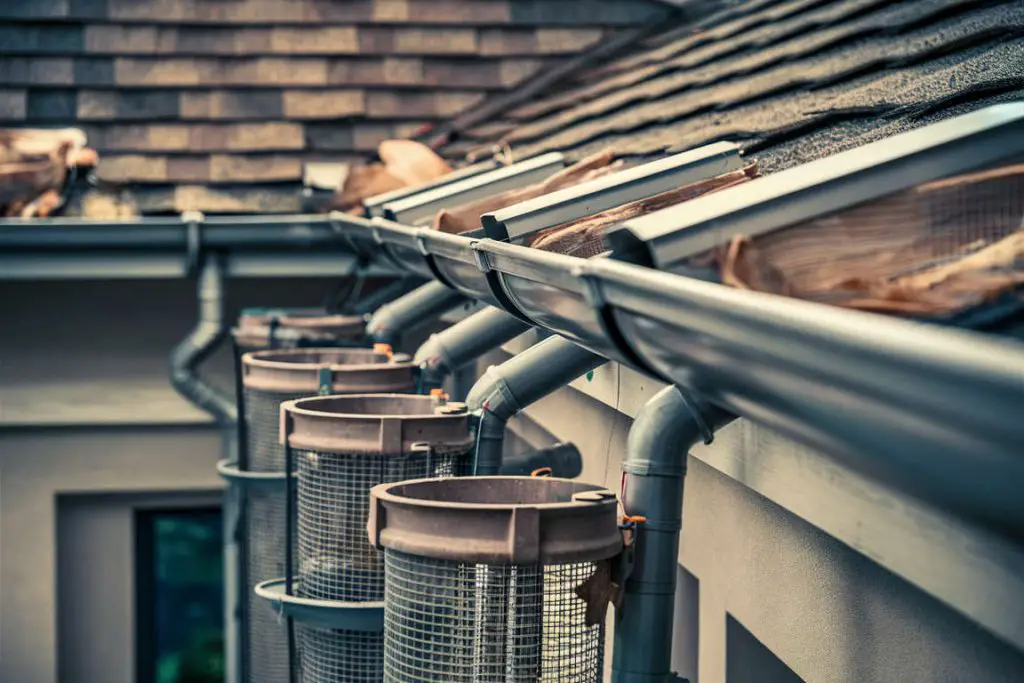

Installing a rainwater collection system involves several detailed steps to ensure efficient operation and clean water. This section breaks down the process into relevant subsections for clarity and ease of implementation.
Setting Up Gutters and Downspouts
Gutters and downspouts are essential components for capturing rainwater from your roof and directing it into storage tanks:
- Gutter Installation: Securely attach gutters along the roof edge to collect rainwater. Ensure they are properly sloped to direct water toward the downspouts.
- Downspout Attachment: Connect downspouts to the gutters to channel the water downward. Position them to lead directly to the storage tanks.
- Debris Protection: Install leaf screens and mesh filters in the gutters and downspouts to prevent leaves and debris from entering the system. These filters help maintain clean water in the storage tanks.
Installing First Flush Diverters
First flush diverters play a crucial role in improving water quality by diverting the initial flow of water, which often contains contaminants from the roof:
- Diverter Placement: Install the first flush diverter at the beginning of the downspout, before the water enters the storage tank.
- Diverter Capacity: Choose a diverter with adequate capacity to handle the first few gallons of runoff, effectively removing debris and contaminants.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean the diverter to ensure it functions correctly, keeping your stored water clean.
Connecting to Storage Tanks
Connecting the downspouts and diverters to the storage tanks is a key step in the installation process:
- Piping Connections: Use durable, UV-resistant pipes or hoses to link the downspouts to the storage tanks. Ensure all connections are tight to prevent leaks and optimize water flow.
- Tank Placement: Position the storage tanks on a stable, level surface close to the downspouts. Elevated platforms can be used to enhance gravity-fed water flow.
- Overflow Management: Install overflow outlets on the storage tanks to handle excess water during heavy rains. Direct overflow water to a safe drainage area or secondary storage.
Setting Up Filtration Systems
Filtration systems are essential for ensuring the collected rainwater is safe for household use:
- Pre-Tank Filters: Install sediment filters before the water enters the storage tanks to remove large particles and debris.
- Post-Tank Filters: Add additional filters between the storage tanks and the household plumbing system. Options include carbon filters and multi-stage systems that remove smaller impurities.
- UV Treatment: Consider installing a UV treatment system to kill harmful microorganisms and ensure the water is safe for drinking and household use.
Ensuring Proper Sealing and Security
Proper sealing and security of the storage system are vital to maintain water quality and system efficiency:
- Tank Sealing: Ensure storage tanks are tightly sealed to prevent contamination and evaporation. Use secure lids or covers to keep out debris and insects.
- Screen Installation: Install screens or mesh at all water entry points to prevent pests from entering the system.
- Security Measures: Implement security measures to protect the system from unauthorized access or tampering. This includes locking mechanisms on tank covers and securing outdoor components.
Final Checks and Testing
After installation, performing final checks and testing the system ensures everything is functioning correctly:
- Leak Inspection: Check all connections, pipes, and tanks for leaks. Address any issues promptly to prevent water loss and maintain efficiency.
- System Testing: Run water through the entire system to ensure proper flow and filtration. Test the water quality to confirm that the filtration and treatment systems are working effectively.
- Adjustments: Make any necessary adjustments to optimize system performance. This includes tweaking the slope of gutters, repositioning tanks, and fine-tuning filtration settings.
Installing a rainwater collection system involves detailed planning and careful execution. Following these steps ensures a reliable and efficient system that provides clean, sustainable water for your household. Regular maintenance and monitoring will keep the system running smoothly and effectively.
Storage and Treatment
Selecting the appropriate storage tanks is crucial for a successful rainwater harvesting system. Tanks should be made from durable, food-grade materials to ensure the water remains uncontaminated. Placement is important; tanks should be situated on a stable, level surface and ideally close to where the water will be used. Covering the tanks helps prevent mosquito breeding and reduces evaporation.
Effective water treatment is essential for household use. Filtration systems remove particulates and impurities from the collected rainwater. Various types of filters are available, including sediment filters, carbon filters, and more advanced multi-stage systems. Each type serves a specific purpose, ensuring the water is clean and free from debris.
In addition to filtration, purification methods are necessary to make the water safe for drinking and other household needs. UV treatment systems are a popular choice, as they effectively kill harmful microorganisms without adding chemicals. Other options include chlorination and ozone treatment, each with its own benefits and considerations. Regular maintenance and monitoring of these systems ensure the water remains safe and of high quality.
Integrating these components effectively will provide a reliable supply of clean water. Regular checks and maintenance are crucial to keep the system running smoothly. Ensuring filters are replaced on schedule and treatment systems are functioning properly will help maintain the water quality, providing peace of mind and a sustainable water source for your household.
Integrating with Household Plumbing
Integrating a rainwater harvesting system with household plumbing involves multiple steps to ensure smooth operation and optimal water use. This section outlines the essential aspects and breaks down the process into relevant subsections for clarity and ease of implementation.
Selecting the Right Pump
A reliable pump is crucial for moving collected rainwater from storage tanks to the household plumbing system. The pump must match your household’s water pressure requirements to ensure consistent flow. Consider the following factors when selecting a pump:
- Capacity and Flow Rate: Choose a pump that can handle the volume of water needed for household use without overloading.
- Pressure Requirements: Ensure the pump provides sufficient pressure to meet the needs of your plumbing fixtures and appliances.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for energy-efficient models to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Connecting to Household Plumbing
Connecting the rainwater system to your home’s plumbing involves technical steps to ensure safe and effective integration:
- Backflow Preventer Installation: A backflow preventer protects the municipal water supply from potential contamination. This device ensures water flows in one direction, preventing any mix-up between rainwater and municipal water.
- Piping and Valves: Install pipes that connect the storage tanks to the household plumbing. Use durable, food-grade materials for safety. Valves control the flow of water, allowing you to switch between rainwater and municipal water as needed.
Setting Up a Dual Plumbing System
A dual plumbing system provides flexibility and ensures a reliable water supply even during periods of low rainfall:
- Switching Mechanism: Valves and control systems can be used to switch between rainwater and municipal water. Automated systems can manage this process based on water availability.
- Secondary Plumbing Lines: Set up secondary lines dedicated to rainwater for specific uses like toilets, washing machines, and outdoor irrigation. This setup helps prioritize rainwater use where it’s most beneficial.
Monitoring Water Levels and Quality
Effective monitoring is essential to ensure a reliable and safe water supply:
- Sensors and Gauges: Install sensors in the storage tanks to monitor water levels. Automated systems can alert you when water levels are low or when maintenance is needed.
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular water quality tests to ensure the collected rainwater remains safe for household use. Testing for contaminants and pathogens helps maintain water safety and quality.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance keeps the system running efficiently:
- Pump Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain the pump to ensure it operates efficiently. Clean the intake and check for wear and tear.
- Pipes and Valves: Inspect pipes and valves for leaks or blockages. Ensure all connections remain secure and functional.
- System Checkups: Schedule periodic checkups to assess the entire system’s condition. Regular inspections help identify and resolve potential issues before they become major problems.
Integrating a rainwater harvesting system with household plumbing involves careful planning, technical knowledge, and regular maintenance. Following these guidelines ensures a reliable and sustainable water supply for your home, promoting environmental conservation and self-sufficiency.
Maintenance and Monitoring
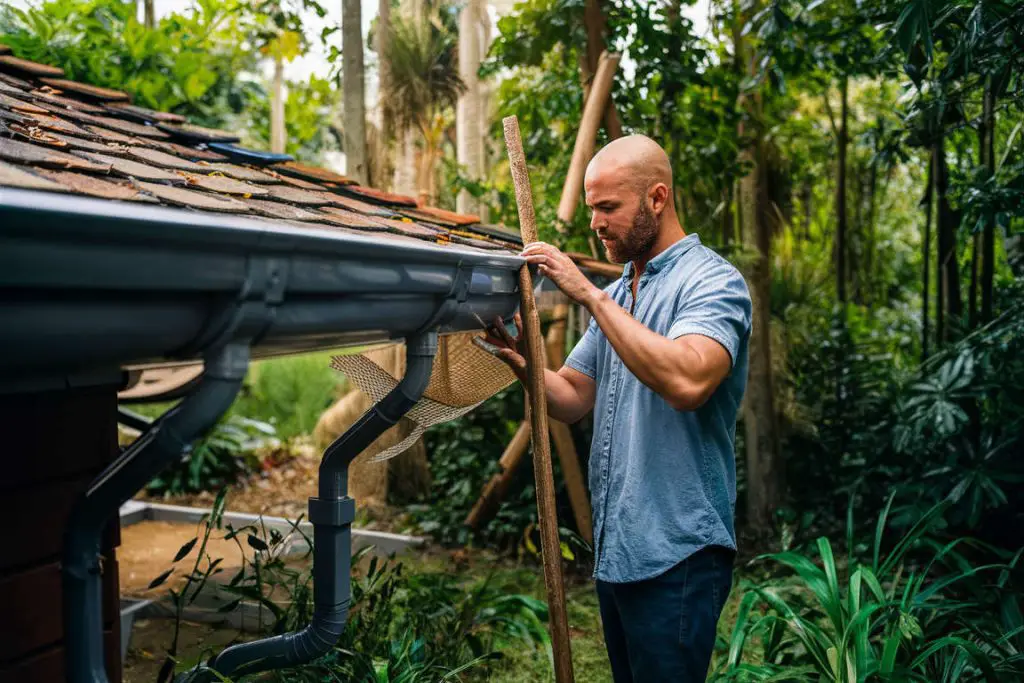

Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your rainwater harvesting system in optimal condition. Cleaning gutters and downspouts periodically prevents debris buildup, ensuring smooth water flow into the storage tanks. Inspecting these components for any damage or clogs will help maintain their efficiency.
Storage tanks also require attention. Draining and cleaning the tanks annually can prevent sediment buildup and algae growth. Using a brush or pressure washer, scrub the interior of the tanks thoroughly, then rinse and refill them to maintain water quality.
Filtration and purification systems need consistent upkeep. Filters should be checked and replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Monitoring the UV treatment system, if used, ensures it remains effective in eliminating harmful microorganisms. Regularly inspecting and maintaining these systems will help provide a continuous supply of clean water.
Water quality testing is a crucial part of the maintenance routine. Conduct tests at least twice a year to check for contaminants and ensure the water is safe for household use. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities and water quality results will help track the system’s performance over time.
Effective monitoring and maintenance of your rainwater harvesting system will ensure its longevity and reliability. A well-maintained system provides a sustainable and safe water source, reducing reliance on municipal water and supporting a more eco-friendly lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
Implementing a comprehensive rainwater collection system for household use offers numerous benefits. Reduced dependency on municipal water, lower water bills, and a reliable alternative water source are just a few advantages. A well-designed and maintained system provides clean, chemical-free water for drinking, cooking, and bathing.
Adopting rainwater harvesting contributes significantly to environmental conservation. Every drop of rainwater collected and used helps reduce the strain on municipal water supplies. Sustainable practices like these play a crucial role in preserving our planet’s resources for future generations.
Starting with careful planning and choosing the right components is essential for a successful setup. Regular maintenance and monitoring ensure the system remains efficient and reliable. Embracing rainwater harvesting not only supports a sustainable lifestyle but also promotes self-sufficiency and resilience.
Encouraging others to consider rainwater collection systems can amplify the positive impact. Sharing knowledge and experiences can inspire more people to adopt this eco-friendly practice. Together, small steps toward sustainability can lead to significant changes for our environment and our communities.
