The Gardening Calendar: What It Is and Why It Is Important
The natural gardening calendar is the season-by-season and month-by-month weather pattern that determines what gardening tasks mother nature usually allows you to perform in your garden at a given time of year.
Gardeners can use this knowledge to create a comprehensive schedule that takes into account the various tasks that need to be done in the garden and when they should be done to achieve the best possible results. Understanding the gardening calendar is crucial for gardeners, as it helps them make the most of their time and resources.
Many gardeners organize their calendars according to the months of the year, and each month has its own set of tasks and activities that need to be completed. These tasks can vary depending on the climate and location of the garden, as well as the type of plants being grown.
How the Months of the Year Affect Gardening

The months of the year have a significant impact on gardening, as each month brings its own set of challenges and opportunities. For example, the gardening tasks that need to be done in January will be different from those gardening tasks required in May. By understanding the specific gardening tasks that should be done each month, gardeners can ensure that their plants thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
January to March
During the winter months of January to March, gardeners can begin preparing their gardens for spring. This involves tasks such as cleaning up debris, pruning trees and shrubs, and applying compost or other organic matter to the soil. Gardeners can also sow early crops such as peas, spinach, and lettuce indoors or in a cold frame.
April to June
In the spring months of April to June, the weather begins to warm up and gardeners can start planting warm-weather crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and beans. This is also the time for watering and weeding, as well as monitoring for pests and diseases. Gardeners should also be aware of the last frost date in their area and take steps to protect their plants from late frosts.
July to September
During the summer months of July to September, gardeners can focus on harvesting and preserving their crops. This involves tasks such as picking fruits and vegetables at the right time, drying or canning them, and storing them properly. Gardeners can also begin preparing for fall by planting crops such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage.
October to December
In the fall months of October to December, gardeners can begin cleaning up their gardens and preparing for winter. This involves tasks such as removing dead plants, applying mulch or other protective coverings to the soil, and planting cover crops such as winter rye. Gardeners can also take advantage of the cooler weather to plant garlic, onions, and other cool-season crops.
How the Gardening Calendar Varies in Different Climate Zones
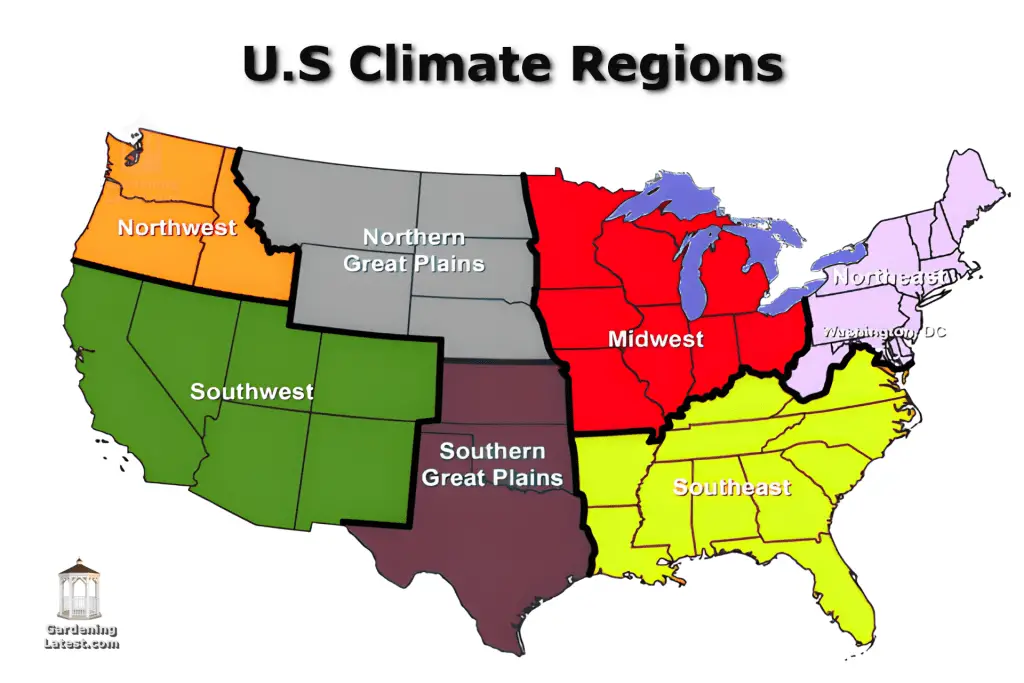
The gardening calendar can vary significantly depending on the climate zone in which the garden is located. Different regions have different weather patterns and temperatures, meaning different planting schedules and gardening tasks based on factors such as temperature, precipitation, and soil conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult a gardening calendar that is specific to your local area and climate zone.
Warm Climate Zones
In warm climate zones such as the southern United States, gardening can be done year-round. These regions have mild winters and long growing seasons, which allow gardeners to grow a wide variety of crops. In warm climates, gardeners can plant warm-weather crops such as tomatoes and peppers in early spring, and continue planting throughout the year.
Temperate Climate Zones
In temperate climate zones such as the Midwest and Northeast United States, gardening is typically done from spring to fall. These regions have distinct seasons and occasional frosts, which limit the growing season. In temperate climates, gardeners typically plant warm-weather crops such as tomatoes and peppers in late spring or early summer and focus on harvesting and preserving their crops in the fall.
Cold Climate Zones
In cold climate zones such as northern Canada and Alaska, gardening is limited to a short growing season in the summer months. These regions have harsh winters and short summers, which require gardeners to make the most of their time. In cold climates, gardeners typically plant cool-season crops such as peas and lettuce in early spring and focus on harvesting and preserving their crops before the first frost.
Unseasonal Weather Patterns in Gardening
With gardening, where every sprout and bloom is often meticulously planned, unseasonal weather patterns can introduce a layer of complexity and unpredictability to your gardening calendar. It is not only meteorological phenomena, such as El Nino, that can disrupt the gardening calendar, but as the climate evolves, and unseasonal weather patterns seemingly become more common, your garden calendar might experience more regular disruption.
Beyond the Traditional Gardening Calendar
Your zucchinis, anticipating a warm embrace, might be met with an untimely frost, while your autumnal chrysanthemums could be confused by a sudden heatwave. These unexpected guests, arriving in the form of early frosts, delayed springs, or erratic rainfall, demand a gardener to be not just a cultivator, but a keen strategist, adept in managing the whims of weather.
Crafting Resilience: Strategies Amidst Weather Anomalies
Building resilience in your garden involves adopting a multifaceted approach. Introduce plant varieties with a spectrum of weather tolerances, ensuring that unexpected weather doesn’t spell disaster for your entire crop. Employ protective measures, such as mulches for sudden cold snaps or shade cloths during unexpected heat, to shield your plants from the elements.
Harnessing Technology: A Modern Ally for Traditional Practices
Incorporate technology and data to navigate through the unpredictability. Leverage weather forecasting tools, and employ apps that provide real-time alerts for various weather anomalies. This integration of technology allows you to preemptively manage risks, safeguarding your garden from unforeseen meteorological challenges.
Final Thoughts
A gardening calendar is an indispensable tool for any gardener, whether they are a beginner or an experienced grower. By understanding how the months of the year affect what needs to be done, ie, gardening jobs for November being different from those gardening tasks in February in the garden, gardeners can plan ahead and ensure that their plants receive the care and attention they need to thrive.
It is clear that to ensure you have the best and most productive garden possible, it is essential to adapt the gardening calendar to the specific climate and weather patterns of the region, gardeners can ensure that their plants thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
Overall, the gardening calendar serves as a guide for gardeners, helping them stay organized and on track with their gardening tasks. By following the gardening calendar, gardeners can ensure that their plants are healthy and productive and that they are able to enjoy a bountiful harvest throughout the year.
Notes/Further Reading:
- Oregon State University: Monthly Garden Calendars
- University of Minnesota: Planting and growing guides
- Michigan State University: Garden calendar
- University of Florida: Florida Gardening Calendar











